Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis
Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Constant Angular Velocity, Constant Angular Acceleration and, Kinematics of Pure Rotational Motion
Important Questions on Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis
A potter's wheel is rotating with a constant acceleration of . How many revolutions will it make in ? The wheel was initially at rest.
A rigid body under pure rotation is uniformly accelerated.The tangential acceleration of a particle of the body, the distance of the particle from the axis, and the angular acceleration of the body are related as . Thus:
If a rigid body rotates through equal angles in equal time intervals, the body is said to rotate with constant angular acceleration.
Define constant angular velocity.
Starting from rest, a fan takes to attain the maximum speed of revolutions per minute. Assuming constant acceleration, find the time taken by the fan in attaining half the maximum speed.
An object changes its rotational speed from to in . Find the angular acceleration of the object?
A merry-go-round has a uniform angular acceleration of . Find the angle through which the merry-go-round rotates if it started from rest and accelerated for seconds.
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with
A ring of radius is rotating with an angular velocity and then it is placed on a rough horizontal surface in vertical plane. The coefficient of friction between the surface and the ring is . How much time it will take to reduce its angular speed half ?
Find the initial angular acceleration of the rod just after when the string is cut.
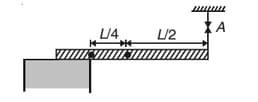
A drum of radius, carrying the load is rigidly attached to a pulley of radius, carrying the load , as shown. At time, the load moves with a velocity of (downward) and a constant acceleration of (downward). Over the time interval, determine:
Cotyledons are also called-
A constant power is supplied to a disc that can rotate freely about a fixed vertical axis. Angular velocity of the disc varies with the number of rotations made by the disc after starting from rest as . Hence is: (K is a constant)
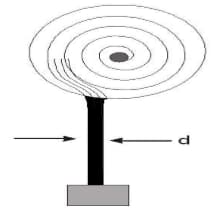
A mass attached to the end of a flexible rope of diameter is raised vertically by winding the rope on a reel as shown. If the reel is turned uniformly at the rate of . What is the tension in rope. The inertia of rope may be neglected.
A particle at rest is to reach an angular velocity of in , with a constant angular acceleration. The total angle turned during this interval is
A block of mass hangs from the rim of a wheel of radius . On releasing from rest the block falls through height in second. The moment of inertia of the wheel is
The moment of inertia of a fly wheel is which is initially stationary. A constant external torque 5Nm acts on the wheel. The work done by this torque during 10 seconds is
A body is in pure rotation. The linear speed v of a particle, the distance r of the particle from the axis and the angular velocity of the body are related as . Thus :
A flywheel rotates with a uniform angular acceleration. Its angular velocity increases from to in 10 s. how many rotations did it make in this period?
A meter stick is hold vertically with one end on the floor and is then allowed to fall. Assuming that the end on the floor the stick does not slip, the velocity of the other end when it hits the floor, will be
